Isosceles and equilateral triangles
We’ve learned that you can classify triangles in different ways. Well, some of these types of triangles have special properties!
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides that are congruent. These two sides are called legs. The remaining side is called a base. Since two sides are congruent, it also means that the two angles opposite those sides are congruent. These would be the two base angles. Here are some diagrams that usually help with understanding.
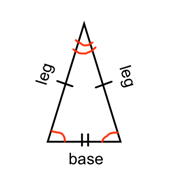
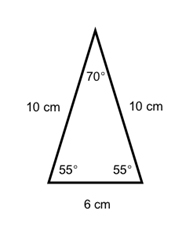
Equilateral Triangle
In an equilateral triangle, all sides are congruent AND all angles are congruent. When all angles are congruent, it is called equiangular. The sides can measure anything as long as they are all the same. The angles, however, HAVE to all equal 60°. This is because all angles in a triangle always add up to 180°and if you divide this amongst three angles, they have to each equal 60°. So, in EVERY equilateral triangle, the angles are always 60°.
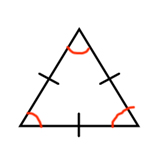
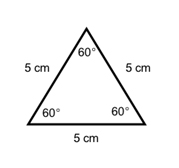
Let’s see if we can put these properties to work and answer a few questions. You have to look at these problems as “puzzles” because sometimes you need to find a part that they are not asking for in order to find the final result. Find a piece at a time and put them together until you reach your answer!
Example 1:
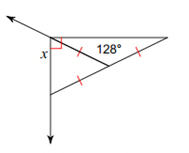
Find x.
There’s actually at least three different ways that you can answer this problem. I’ll show you one. They ultimately want to find the measure of that exterior angle.
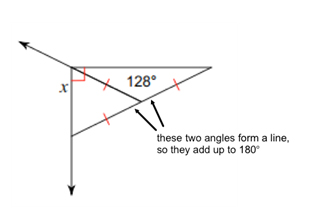 \({\text{180 - 128 = 52}}\)
\({\text{180 - 128 = 52}}\)
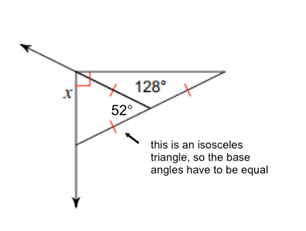 \({\text{180 - 52 = 128}}\)
\({\text{180 - 52 = 128}}\)
\({\text{128}} \div {\text{2 }} = {\text{ 64}}\)
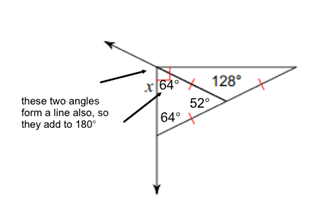 \({\text{180 - 64 = 116}}\)
\({\text{180 - 64 = 116}}\)
\({\text{x }} = {\text{ 116}}^\circ \)
Example 2:
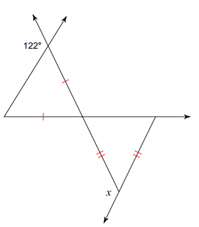
This is going to take a few steps. We need a few pieces of the puzzle before we can find the measure of x.
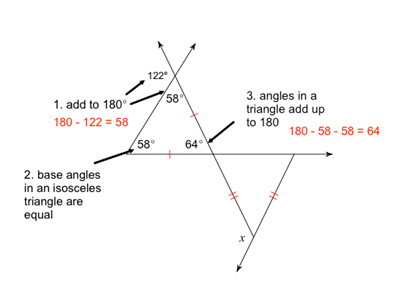
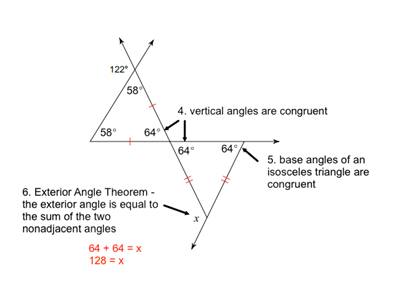
If you don’t remember that last step, don’t worry! You can just take two more steps and find the 3rd angle of the bottom triangle and subtract it from 180°to find the exterior angle.
Many of these problems take more than one or two steps, so look at it as a puzzle and put your pieces together!
Below you can download some free math worksheets and practice.
Find the value of x.
This free worksheet contains 10 assignments each with 24 questions with answers.
Example of one question:
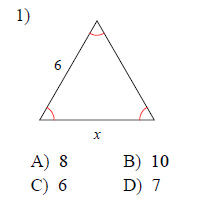
Watch below how to solve this example:
Find the value of x.
This free worksheet contains 10 assignments each with 24 questions with answers.
Example of one question:
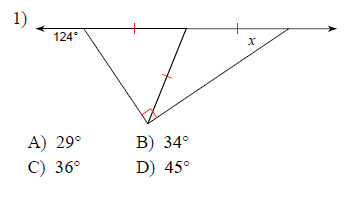
Watch below how to solve this example:
Find the value of x.
This free worksheet contains 10 assignments each with 24 questions with answers.
Example of one question:
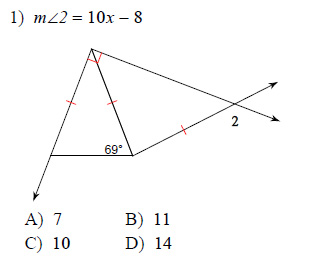
Watch below how to solve this example:


