Line segment constructions
Constructing lines can be more difficult than it sounds. You will need a protractor and a compass.
Congruent lines have the same measure. Most protractors have a ruler on the flat edge that you can use.
Here are the steps to constructing a congruent line segment.
Carefully measure the first segment using the ruler part of the protractor (or using a ruler).
- To draw the congruent segment, mark the endpoint at zero and another endpoint to match the measurement of the first line segment.
- Using the straightedge, connect the two points.
A perpendicular bisector is a line that divides another line into two equal parts at a right angle.
Here are the steps to constructing a perpendicular bisector of a line.
- Set the width of the compass to a little more than half of the total line (the width doesn’t matter so much, as long as it does not change during this step)
- Put the point of the compass on one endpoint of the line and use the pencil side to draw a small arc on the top and the bottom of the line.
- Without changing the width, repeat this step using the other endpoint of the line.
- The arcs should intersect at a point above and a point below the line. Using the ruler, connect these points with a straight line. This is your perpendicular bisector.
Parallel lines have the same slope and will never intersect. These can actually be a bit difficult to construct.
Here are the steps to constructing a parallel line.
- Draw a point somewhere on your first line that is not directly below the point that you will be drawing the new parallel line. Make the point a good amount to either the left or the right.
- Using the straightedge, draw a line connecting your new point and the point for the parallel line. This line is called a transversal.
- Using your compass, draw an arc through the first line and the transversal. The pointy part of the compass should be on the point that you created in step 1.
- Without changing the width of the compass, draw a similar arc using the point for the new parallel line.
- Set the compass width to match where the first arc intersects with the transversal and with the original line.
- Don’t change the compass, and move it to the second arc. The pointy part of the compass should be on the intersection of the arc with the transversal and use the pencil part to draw a small arc through the arc that you made in step 5.
- Using the straightedge, connect this intersection with the point for your parallel line.
Construct a line segment congruent to each given line segment.
This free worksheet contains 10 assignments each with 24 questions with answers.
Example of one question:
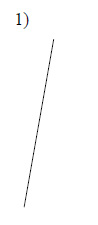
Watch below how to solve this example:
Construct the perpendicular bisector of each.
This free worksheet contains 10 assignments each with 24 questions with answers.
Example of one question:
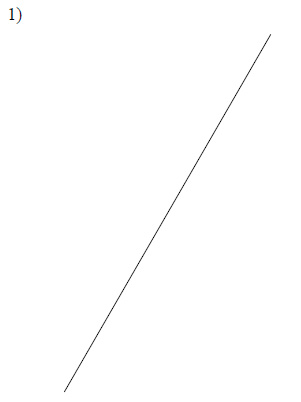
Watch below how to solve this example:
Construct a line segment through the given point parallel to the given line segment.
This free worksheet contains 10 assignments each with 24 questions with answers.
Example of one question:

Watch below how to solve this example:


